![[E SCRAP Dealer], we're commit](https://bizimages.withfloats.com/tile/697857319e433c6c66008818.jpg)
Electronic waste, also known as e-waste, refers to...
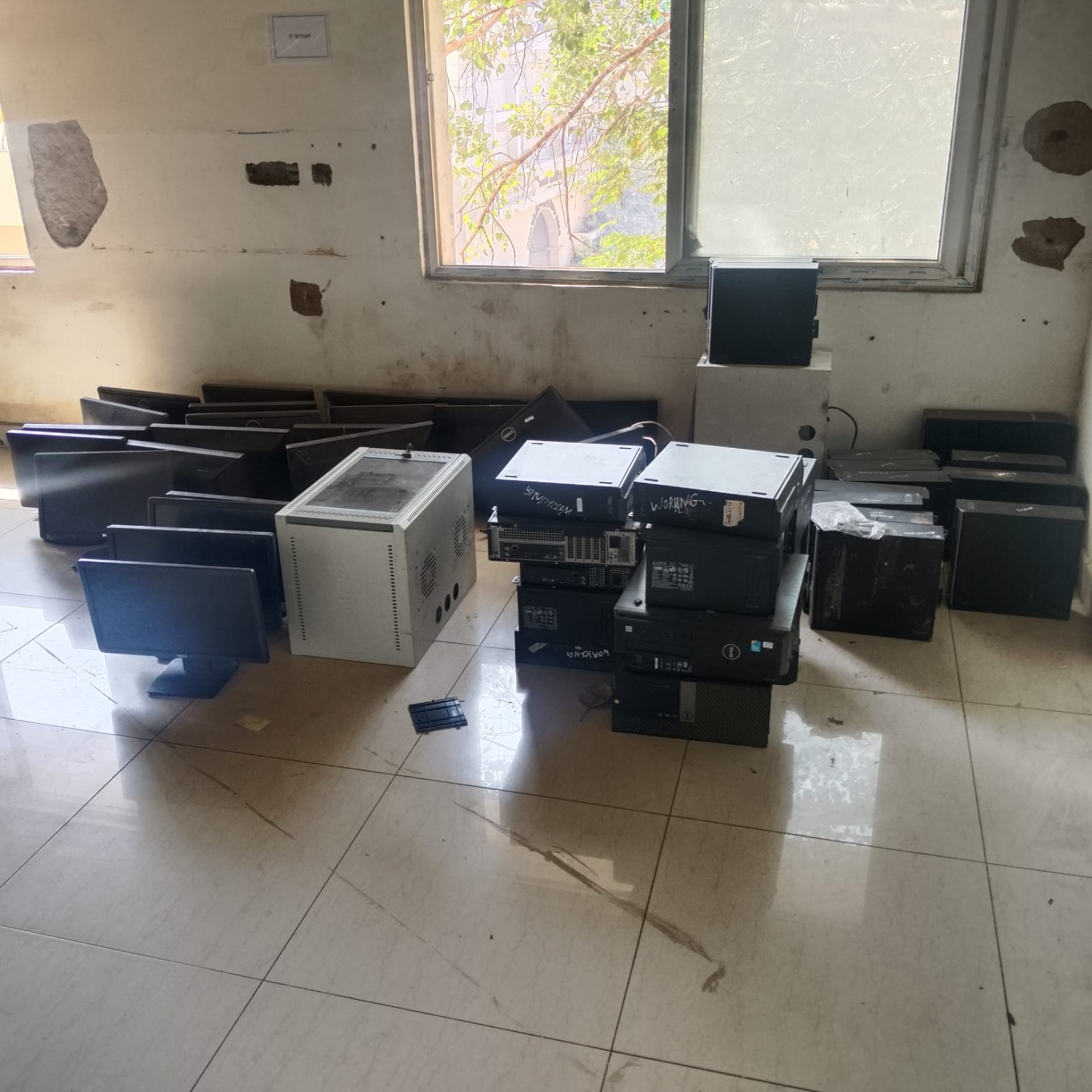

Electronic waste, also known as e-waste, refers to any discarded electronic devices or equipment. Some common examples of e-waste contents include: 1. Computers and laptops: This category includes both desktop computers and laptop computers that are no longer in use. It also includes their accessories such as keyboards, mice, and computer monitors. 2. Mobile phones and tablets: Old or broken smartphones, tablets, and their chargers are significant contributors to e-waste. 3. Televisions and monitors: Old CRT (cathode-ray tube) televisions and monitors, as well as newer LED and LCD screens, make up a significant portion of electronic waste. 4. Printers and copiers: Discarded printers, photocopiers, and their ink cartridges contribute to e-waste, especially due to their relatively short lifecycle. 5. Audio and video equipment: Old or damaged stereos, speakers, headphones, DVD players, and other audio and video equipment add to the e-waste stream. 6. Appliances: Outdated kitchen appliances such as refrigerators, washing machines, microwave ovens, and air conditioners contain electronic components that contribute to e-waste when they are disposed of. 7. Batteries: Disposable batteries, rechargeable batteries, and the batteries used in electronic devices are considered hazardous waste and pose environmental risks if not properly managed. 8. Gaming consoles: Old gaming consoles, accessories, and game cartridges contribute to electronic waste when they are no longer in use. 9. Cables and cords: Discarded cables, power cords, and adapters add to the e-waste problem since they are often difficult to recycle due to their composition. 10. Other electronic accessories: Various other electronic accessories such as camera equipment, GPS devices, smartwatches, and fitness trackers also contribute to e-waste.
Keywords
Subscribe for latest offers & updates
We hate spam too.